Stainless Steel Manufacturing Process
1

1. Infrastructure
Raw materials used are
stainless steel scrap, iron, nickel and chromium.
2

2. EAF
These substances are added into an
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) where electrodes heat the mix to its melting point.
3

3. AOD Converter
The mix is then treated in Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD) Convertor where pipes blast Argon and Oxygen gases into it.
The AOD minimises undesired oxidation and removes excess carbon from the mix.
4

4. Vacuum Oxygen Decarburization
The mix is then treated in a tank degassing unit which is additionally equipped with an oxygen blowing lance. Due to reduced carbon monoxide partial pressure under vacuum condition, this process helps in
reducing the carbon content of high alloyed stainless steel grades.
5

5. Continuous Casting
The stainless steel mix is
cast into stainless steel slabs and blooms through a process called continuous casting.
6

6. Grinding
The stainless steel slabs/blooms go through a
grinding process to remove any surface defect that has occurred during casting.
7

7. Reheating
The stainless steel slabs are then reheated due to which a rusty scale (oxide) is accumulated on the surface. This scale is removed from the surface by
high pressure water jets in a process called as Descaling
8

8. Roughing Mill
The stainless steel slab is then sent back and forth through the Roughing Mill to
reduce its thickness and increase its length, without changing its width.
9
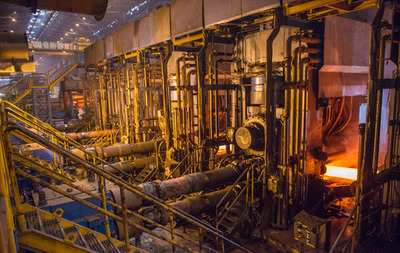
9. Finishing Mill
Having acquired the shape of a sheet, it is now sent to
further thinning in the Finishing Mill, depending on customer' requirement.
10

10. Coiling
These stainless steel slabs are now turned into plates (~20 mm thickness) or coils (~6 mm thickness) as per order after
several intermediate processes.
11

11. Annealing
The hot rolled (HR) coil undergoes a thermal process called annealing, in which the metal is given a consistent, uniform internal structure and homogeneous properties. This helps to
improve the mechanical stability and corrosion-resistance of the coil.
12

12. Pickling
The stainless steel coil then goes through a chemical process, Pickling, in which mill scales,
surface oxides, and annealing oxides are removed.
13

13. Quality Testing
There is quality testing at each stage of production, where a sample is taken from the product, and sent to labs for physical and chemical examination.
Each gram of our stainless steel is planned to perfection.
14

14. HRAP/CRAP Coils
The resultant product is called Hot Rolled Annealed Pickled (HRAP) stainless steel coil which goes either directly to the customer, or to be made into
15

15. Customization
CRAP coil goes through several production processes aimed at customising surface finish, thickness, product chemistry and mechanical properties.
Different kinds of stainless steel finishes such as CR, BA, and 2D/2B are produced during these processes.
16

16. Slitting
The stainless steel coils in Cold Rolling Division are reduced to
different widths as per the customer requirement.
17

17. SPD
For specialized applications and products such as coin blanks, strips for razor blades, and precision strips up to 0.05 mm thickness, our Special Product Division produces
highly sophisticated stainless steel products.

